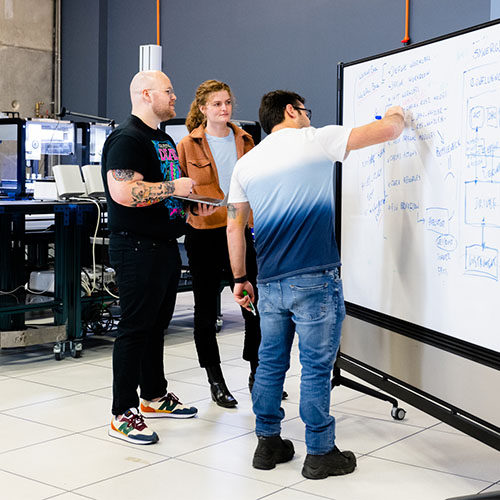
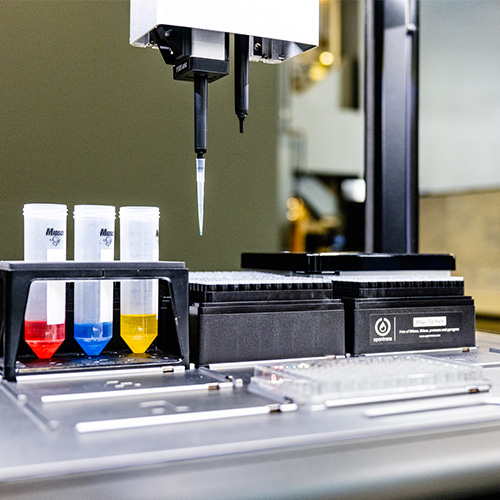
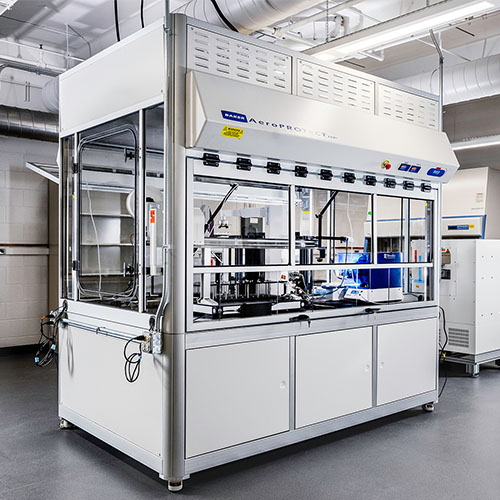
The MEDAL project, which stands for Mobilizing the Emerging Diverse AI Talent, brings together expertise in large language models, virtual reality, and robotic automation to produce collegiate-level coursework focused on using these tools to design and establish automated scientific laboratories.
Project Leaders:
Dr. Sumit Kumar Jha – Lead PI, University of Texas San Antonio
Dr. Arvind Ramanathan – ANL Partner and Co-PI, Argonne National Laboratory
Dr. Sreenivasan Ramamurthy – Co-PI, Bowie State University
Dr. Sunny Raj – Co-PI, Oakland University
Dr. Sathish Kumar – Co-PI, Cleveland State University
Dr. Giri Narasimhan – Co-PI, Florida International University
Dr. Rickard Ewetz – Co-PI, University of Central Florida